“Applied kinesiology is something that can be performed with knowledge, with physiological facts, and with predictable certainty. It should be done, it can be done.”
– George J. Goodheart, Jr. D.C., DIBAK
We have collected some of the common ailments and problems that one may encounter. We briefly discuss the symptoms, description, probable causes, standard treatment and the AK (Applied Kinesiology) approach. This may help with making a more informed decision on the type of treatment model best for you.
Lower Body
Achilles
Achilles Tendonitis
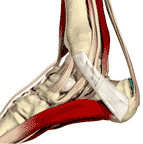 Signs or Symptoms
Signs or Symptoms
Pain in the Achilles tendon with up and down movement of the foot at the ankle.
Description
Inflammation of the tendon of the calf muscles. This causes restriction of motion and pain, ache and tenderness when walking or even touching the tendon.
Causes
Over utilization, such as too much running, especially hills. Trauma, such as a kick to the tendon, is another common cause. Shoe pressure can aggravate the tendon. The most common cause is an over contraction of the muscles, calf muscles, that attach to the tendon.
Standard treatment
Heel lifts to reduce the pressure, stretching exercises and anti inflammatory medications
AK Approach
Muscle balance is the goal of the treatment. In this condition, abnormal stresses are applied to the tendon causing the tendonitis. To treat this condition, proper muscle function must be returned. This can involve many different muscle therapies ranging from massage to changing the way you walk and run. Other lifestyle modifications are used to prevent or minimize exacerbating the condition. A specific program for your needs is created.
ACL
Anterior cruciate ligament - ACL
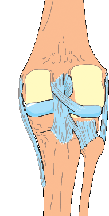 Signs or Symptoms
Signs or Symptoms
Pain in the knee with instability
Description
Injury to this ligament occurs when the person suddenly pivots causing excessive rotational forces on the ligament. Other causes are severe trauma and work injuries. When the injury occurs, the person will usually describe a feeling of the knee giving out, or collapsing. They also say they hear a 'pop'.
Causes
Sever trauma is the most common cause. However, there can be slow stretching of the ligament due to repetitive stress caused by other mechanical factors related to improper ankle foot Ð knee muscle function Ð or pelvic mechanical defects.
Standard treatment
Rest, bracing and exercises to increase muscle strength. If the tear is great, then surgical repair is done.
AK Approach
In an injury to the anterior cruciate ligament you will usually find other supporting ligaments, muscles, and skin being damaged. Treatment begins by assessing exactly which structures have been injured and then directing appropriate therapy to those injured structures. The second phase of therapy is to reestablish normal muscle coordination and strength. Again, there are a number of different techniques that can be used. Testing is used to prepare a specific program for your needs.
Ankle
Ankle Sprains
 Signs or Symptoms
Signs or Symptoms
Swelling, bruising and pain around the ankle following a sudden twisting injury.
Description
Injury occurs when the ankle is twisted inward, and the outer, or lateral, ligaments are stretched too far. As these ligaments are stretched further than normal, some may tear causing the pain associated with ankle sprains.
Causes
Sudden twisting injury as in landing on the side of your foot or slipping off of a curb.
Standard treatment
Rest, ice, taping. If the ligaments are totally torn then surgery to repair or a cast may be needed
AK Approach
The adage once a sprain always a sprain has been proven wrong. In a sprain of the ankle, many of the supporting ligaments, muscles, and skin become damaged. Treatment begins by assessing exactly which structures have been injured and then directing appropriate therapy to those injured structures. The second phase of therapy is to reestablish normal muscle coordination and strength. Again, there are a number of different techniques that can be used. Testing is used to prepare a specific program for your needs.
Chondromalacia
Chondromalacia
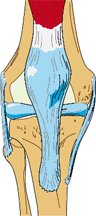 Signs or Symptoms
Signs or Symptoms
Tenderness, ache or pain around and under the kneecap
Description
The cartilage under the kneecap breaks down due to misuse
Causes
Malformation of the bone, overuse, muscular imbalances
Standard treatment
Anti-inflammatories, cortisone, stretching
AK Approach
Testing is done to determine muscle imbalances around the knee. Excessive stress can also come from imbalances in the foot and ankle and in the pelvis. Specific muscle therapies are used to normalize the muscle actions around the knee and especially the patella, kneecap. . Nutritional therapies aimed at decreasing inflammation are utilized Following this a rehabilitative program to develop equal muscle strength reinforced with a nutritional program to maximize muscle and cartilage regeneration are used. Other lifestyle modifications are used to prevent or minimize exacerbating the condition. A specific program for your needs is created.
Footpronation
Pronation - Dropped Arch
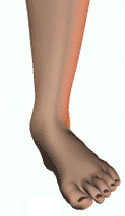 Signs or Symptoms
Signs or Symptoms
Pain or chronic ache in the ankle. Instability when walking. Frequent ankle sprains.
Description
Over-pronation is a common biomechanical problem that occurs in the walking process when your arch collapses on weight bearing. This causes inflammation of the plantar fascia, causing severe discomfort and leading to other foot problems.
Causes
Obesity, pregnancy or repetitive pounding on a hard surface can weaken the arch leading to dropping of the arch.
Standard treatment
Orthotics are fitted to correct the dropping of the arch.
AK Approach
The muscles of the foot and ankle are evaluated for proper function. Corrections are aimed at normalizing the muscle functioning of the foot. Therapy is then aimed at strengthening the ligaments and muscles of the foot and the need for orthotic support. Nutritional therapies aimed at increasing factors that would lead to relaxing the muscles and reducing any inflammation is considered.
Other lifestyle modifications are used to prevent or minimize exacerbating the condition. A specific program for your needs is created.
ITB
Iliotibial band syndrome (ITB). Outside of the upper leg pain
Signs or Symptoms
Ache or pain running down the outside of the upper leg.
Description
Inflammation of the hard fibrous band running down the outside of the upper leg so that it does not glide as you walk and bend. The irritation usually occurs over the outside of the knee joint.
Causes
Sudden increase in the level of training in athletes, or those who suddenly start excessive walking routines. Most individuals have a mechanical problem with their gait. Excessive pronation is another cause as is having a difference in their leg length and people who are bow-legged.
Standard treatment
Ice, stretching, anti-inflammatory medications and possibly cortisone injections and surgery.
AK Approach
The ITB is over contracting and the muscle imbalances and structural problems that are causing this must be normalized. The muscles that support the pelvis are evaluated to find the ones that are malfunctioning. These are corrected and then the alignment of the pelvic bones is corrected. The attention is then shifted to the localized structures that are injured and failing to support the pelvic joints properly. These can include specialized treatments for ligaments, muscles, skin and joints. As factors as far away as the foot and ankle can cause torsion that adversely affects the ITB, the examination must include these areas and corrective procedures done to normalize any abnormal torsion in the lower extremity. This is followed by an analysis of how the person walks, moves and their occupational positions. Nutritional therapies aimed at increasing factors that would speed healing and reduce any inflammation are considered.
Other lifestyle modifications are used to prevent or minimize exacerbating the condition. A specific program for your needs is created.
Jumpknee
Jumper
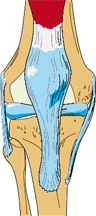 Signs or Symptoms
Signs or Symptoms
Sharp pain or ache just below the kneecap that occurs after activities that cause stress on the tendon. A few of these activities are jogging, climbing stairs, jumping or hill climbing.
Description
Patellar tendonitis is when the tendon and the tissues that surround it, become inflamed and irritated. This is usually due to overuse, especially from jumping activities.
Causes
Overuse is blamed as the cause of patellar tendonitis, however on examination there are usually muscle imbalances that are the underlying cause of why you get this condition and another person doesn't.
Standard treatment
Avoidance of activities that aggravate the problem is the first step. Anti-inflammatory medications are used. Stretching exercises are usually given.
AK Approach
The patellar tendon can be injured by either immediate direct trauma or by repeated micro trauma. If the injury occurred from a single trauma, the examination is directed immediately to the severity of the injury and is surgery indicated. Otherwise, the examination is more general as to the total functioning of the lower extremity. As the knee can be adversely affected by problems in the ankle and foot or the pelvis above it, the examination begins by looking for factors in these areas that would adversely affect knee stability. Locally, the stability of the major ligaments of the knee are then tested for. The muscles that support the knee are evaluated to find the ones that are malfunctioning. These are corrected and then tested for the need of corrective exercises. The attention is then shifted to the localized structures that are injured and failing to support the knee joint properly. These can include specialized treatments for ligaments, muscles, skin and joints. Finally, attention is directed to corrective procedures that can help coordinate the muscles to help prevent future injuries. Nutritional therapies aimed at increasing factors that would speed healing and reduce any inflammation are considered.
Other lifestyle modifications are used to prevent or minimize exacerbating the condition. A specific program for your needs is created.
Knee Problems
Knee
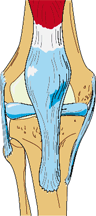 Signs or Symptoms
Signs or Symptoms
Range from mild discomfort to inability to bend, locking of the knee or unexpected collapse to severe pain
Description
The knee is a complex structure of ligaments, cartilage, specialized cartilage called meniscus, muscles and four bones (tibia, femur, fibula and patella) that must all work in coordination
Causes
Trauma is an obvious factor as in athletic injuries. Slow overuse and leads to degeneration Ð arthritis, hardening of the cartilage, degeneration of the cartilage, and consequently inflammation.
Standard treatment
Physical therapy is aimed at increasing mobility, stretching shortened muscles and strengthening weak muscles. Inflammation reduction is the aim of most medications given. Surgery is done to repair ligaments, clean out pieces of broken cartilage or replacing of eh total knee.
AK Approach
As the knee can be adversely effected by problems in the ankle and foot or the pelvis above it. The examination begins by looking for factors in these areas that would adversely affect knee stability. Locally, the stability of the major ligaments of the knee are then tested for. The muscles that support the knee are evaluated to find the ones that are malfunctioning. These are corrected and then tested for the need of corrective exercises. The attention is then shifted to the localized structures that are injured and failing to support the knee joint properly. These can include specialized treatments for ligaments, muscles, skin and joints. Finally, attention is directed to corrective procedures that can help coordinate the muscles to help prevent future injuries. Nutritional therapies aimed at increasing factors that would speed healing and reduce any inflammation are considered.Other lifestyle modifications are used to prevent or minimize exacerbating the condition. A specific program for your needs is created.
Lowback
Lumbago - Low back pain
 Signs and Symptoms
Signs and Symptoms
Moderate to severe pain in the low back with no radiation to the leg
Description
The muscles and ligaments of the lumbar spine have been strained
Causes
This condition usually follows a lifting type of injury where the person is bent over and suddenly feels something go in the back and the pain comes immediately or within hours of the incident. There is usually swelling from the strain of the fibers of the back. These include muscles and ligaments.
Standard Treatment
RICE - which stands for rest, ice and possibly a support brace. This is accompanied by taking anti-inflammatory medications and at times a muscle relaxant. Failure to respond to this care is followed by physical therapy using ultrasound, muscle stimulation and then at times strengthening exercises if it is chronic.
AK Approach
In addition to most of the standard treatment, the structures of the back are tested to find the ones that were weak that allowed the injury to occur. Specific muscle therapies are used to reduce the spasm muscles and you are taught to do some of these at home. Manipulation is performed to align the pelvis and the lumbar spine to equalize the weight on the disc structures. Dietary recommendations to speed the healing and reduce inflammation are also considered.
MCL
Medial Collateral Ligament (MCL)
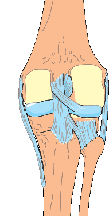 Signs or Symptoms
Signs or Symptoms
Instability of the inside of the knee with ache, pain, tenderness and swelling depending on the degree of injury.
Description
The MCL stabilizes the knee joint and prevents the knee from buckling inwards. The ligament runs across the inside (medial aspect) of the knee in a vertical direction when standing
Causes
Usually it is injured from stress to the outer side of the knee as being hit. It can also occur from repeated stress as in a chronic over pronating ankle or pelvic instability.
Standard treatment
Rest, anti-inflammatory medications and bracing are the most used. Surgery is done when complete tearing of the ligament occurs.
AK Approach
The medial collateral ligament can be injured by either immediate direct trauma or by repeated micro trauma. If the injury occurred from a single trauma, the examination is directed immediately to the severity of the injury and is surgery indicated. Otherwise, the examination is more general as to the total functioning of the lower extremity. As the knee can be adversely effected by problems in the ankle and foot or the pelvis above it. The examination begins by looking for factors in these areas that would adversely affect knee stability. Locally, the stability of the major ligaments of the knee are then tested for. The muscles that support the knee are evaluated to find the ones that are malfunctioning. These are corrected and then tested for the need of corrective exercises. The attention is then shifted to the localized structures that are injured and failing to support the knee joint properly. These can include specialized treatments for ligaments, muscles, skin and joints. Finally, attention is directed to corrective procedures that can help coordinate the muscles to help prevent future injuries. Nutritional therapies aimed at increasing factors that would speed healing and reduce any inflammation are considered. Other lifestyle modifications are used to prevent or minimize exacerbating the condition. A specific program for your needs is created.
Meniscus
Meniscus
Signs or Symptoms
Instability of the knee, locking of the knee, pain or ache on either the inside or outside of the knee
Description
The two most common causes of injuries are due to traumatic sudden injury asis seen in athletes and degenerative problems as seen in older patients who have more brittle cartilage. The most common mechanism of a traumatic meniscus tear occurs when the knee joint is bent flexed) and the knee is then twisted
Causes
The most common mechanism of a traumatic meniscus tear occurs when the knee joint is bent flexed) and the knee is then twisted
Standard treatment
Immediately, ice and immobilization are done. Anti-inflammatories are given. If severe, surgery is indicated.
AK Approach
The meniscus can be injured by either immediate direct trauma or by repeated micro trauma. If the injury occurred from a single trauma, the examination is directed immediately to the severity of the injury and is surgery indicated. Otherwise, the examination is more general as to the total functioning of the lower extremity. As the knee can be adversely affected by problems in the ankle and foot or the pelvis above it, the examination begins by looking for factors in these areas that would adversely affect knee stability. Locally, the stability of the major ligaments of the knee are then tested for. The muscles that support the knee are evaluated to find the ones that are malfunctioning. These are corrected and then tested for the need of corrective exercises. The attention is then shifted to the localized structures that are injured and failing to support the knee joint properly. These can include specialized treatments for ligaments, muscles, skin and joints. Finally, attention is directed to corrective procedures that can help coordinate the muscles to help prevent future injuries. Nutritional therapies aimed at increasing factors that would speed healing and reduce any inflammation are considered. Other lifestyle modifications are used to prevent or minimize exacerbating the condition. A specific program for your needs is created.
Metatarsalgia
Metatarsalgia
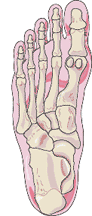 Signs or Symptoms
Signs or Symptoms
Localized moderate to severe pain in the area of the foot just before the toes
Description
Metatarsalgia is a general term used to denote a painful foot condition in the metatarsal region of the foot (the area just before the toes, more commonly referred to as the ball-of-the-foot). This is a common foot disorder that can affect the bones and joints at the ball-of-the-foot.
Causes
It is usually due to excessive pressure over a long period of time. It is often caused from improper fitting footwear, most frequently by womenÕs dress shoes and other restrictive footwear. Footwear with a narrow toe box (toe area) forces the ball-of-foot area to be forced into a minimal amount of space.
Standard treatment
If improper fitting footwear is the cause of the pain, the footwear must be changed. Footwear designed with a high, wide toe box (toe area) and a rocker sole is ideal for treating metatarsalgia. Orthotics are usually fitted. Cortisone injections are the next line of treatment. Surgery is also a possibility.
AK Approach
The muscles that support the foot and ankle are evaluated to find the ones that are malfunctioning. These are corrected and then the alignment of the foot bones is corrected. The attention is then shifted to the localized structures that are injured and failing to support the foot joints properly. These can include specialized treatments for ligaments, muscles, skin and joints. This is followed by an analysis of how the person walks or runs. Depending on the foot ankle complex, orthotics may be needed to support the foot properly. Finally, attention is directed to corrective procedures that can help stabilize and strengthen the structures to help prevent future injuries. Nutritional therapies aimed at increasing factors that would speed healing and reduce any inflammation are considered. Other lifestyle modifications are used to prevent or minimize exacerbating the condition. A specific program for your needs is created.
Patella
Patellar Tendonitis
 Signs or Symptoms
Signs or Symptoms
Sharp pain or ache just below the kneecap that occurs after activities that cause stress on the tendon. A few of these activities are jogging, climbing stairs, jumping or hill climbing.
Description
Patellar tendonitis is when the tendon and the tissues that surround it, become inflamed and irritated. This is usually due to overuse, especially from jumping activities.
Causes
Overuse is blamed as the cause of patellar tendonitis, however on examination there are usually muscle imbalances that are the underlying cause of why you get this condition and another person doesn't.
Standard treatment
Avoidance of activities that aggravate the problem is the first step. Anti-inflammatory medications are used. Stretching exercises are usually given.
AK Approach
The patellar tendon can be injured by either immediate direct trauma or by repeated micro trauma. If the injury occurred from a single trauma, the examination is directed immediately to the severity of the injury and is surgery indicated. Otherwise, the examination is more general as to the total functioning of the lower extremity. As the knee can be adversely affected by problems in the ankle and foot or the pelvis above it, the examination begins by looking for factors in these areas that would adversely affect knee stability. Locally, the stability of the major ligaments of the knee is then tested for. The muscles that support the knee are evaluated to find the ones that are malfunctioning. These are corrected and then tested for the need of corrective exercises. The attention is then shifted to the localized structures that are injured and failing to support the knee joint properly. These can include specialized treatments for ligaments, muscles, skin and joints. Finally, attention is directed to corrective procedures that can help coordinate the muscles to help prevent future injuries. Nutritional therapies aimed at increasing factors that would speed healing and reduce any inflammation are considered.
Other lifestyle modifications are used to prevent or minimize exacerbating the condition. A specific program for your needs is created.
Patellofemoral
Patellofemoral Pain
 Signs or Symptoms
Signs or Symptoms
Pain and ache that occur in the region of the knee cap and extends up the thigh
Description
An imbalance in the functioning of the quadriceps muscle causes tracking problems for the kneecap. This leads to localized inflammation.
Causes
Local trauma, overdevelopment or underdevelopment of sections of he quadriceps, postural abnormalities like a short leg, excessive pronation and pelvic imbalances can be part of the cause.
Standard treatment
Anti-inflammatory medications, stretching exercises and rest.
AK Approach
The quadriceps can be injured by immediate direct trauma, by repeated micro trauma or a nerve problem that causes weakening of the muscle. Testing begins with an attempt to understand the functioning of he different divisions and subdivisions of eh quadriceps muscle. The examination then turns to the total functioning of the lower extremity. As the knee can be adversely affected by problems in the ankle and foot or the pelvis above it, the examination begins by looking for factors in these areas that would adversely affect knee stability. Locally, the stability of the major ligaments of the knee are then tested for. The muscles that support the knee are evaluated to find the ones that are malfunctioning. These are corrected and then tested for the need of corrective exercises. The attention is then shifted to the localized structures that are injured and failing to support the knee joint properly. These can include specialized treatments for ligaments, muscles, skin and joints. Finally, attention is directed to corrective procedures that can help coordinate the muscles to help prevent future injuries. Nutritional therapies aimed at increasing factors that would speed healing and reduce any inflammation are considered.
Other lifestyle modifications are used to prevent or minimize exacerbating the condition. A specific program for your needs is created
Piriformis Syndrome
Piriformis Syndrome Non Disc - Sciatica
Signs or Symptoms
Sciatic pain, pains of unexplained origin in the buttocks, abnormal sensations in the genito-urinary area.
Description
According to the textbooks no one really knows exactly what causes piriformis syndrome, or if it really exists. Some doctors believe that the piriformis syndrome is given to hip/buttock pain that cannot be otherwise diagnosed. Travell, John Kennedy's doctor, believed that the piriformis syndrome is more common than disc problems and a very real cause of pain and disability.
Causes
The piriformis muscle contracts putting pressure on the major nerves in the pelvis
Standard treatment
Stretching exercises, anti-inflammatory medications and deep massage
AK Approach
The piriformis is over contracting and the function of this muscle must be normalized. The muscles that support the pelvis are evaluated to find the ones that are malfunctioning. These are corrected and then the alignment of the pelvic bones is corrected. The attention is then shifted to the localized structures that are injured and failing to support the pelvic joints properly. These can include specialized treatments for ligaments, muscles, skin and joints. This is followed by an analysis of how the person walks, moves and their occupational positions. Finally, attention is directed to corrective procedures that can help stabilize and strengthen the structures to help prevent future over contraction of the piriformis. Nutritional therapies aimed at increasing factors that would speed healing and reduce any inflammation are considered.
Other lifestyle modifications are used to prevent or minimize exacerbating the condition. A specific program for your needs is created.
Plantar Fasciitis
Plantar Fasciitis
 Signs or Symptoms
Signs or Symptoms
Severe pain or ache around the heel bone on the bottom of the foot.
Description
Plantar fasciitis, which is also known as a heel spur, is a painful foot condition. The muscles of the bottom of eh foot become over contracted. This over contraction causes inflammation and is then called plantar fasciitis. The over contraction of the muscles pull on the heel bone and slowly a spur can form on the heel bone.
Causes
Over pronation is the major cause
Standard treatment
Orthotics, cortisone injections
AK Approach
The muscles that support the foot and ankle are evaluated to find the ones that are malfunctioning. These are corrected and then the alignment of the foot bones is corrected. The attention is then shifted to the localized structures that are injured and failing to support the foot joints properly. These can include specialized treatments for ligaments, muscles, skin and joints. This is followed by an analysis of how the person walks or runs. Depending on the foot ankle complex, orthotics may be needed to support the foot properly. Finally, attention is directed to corrective procedures that can help stabilize and strengthen the structures to help prevent future injuries. Nutritional therapies aimed at increasing factors that would speed healing and reduce any inflammation are considered.
Other lifestyle modifications are used to prevent or minimize exacerbating the condition. A specific program for your needs is created.
Sacroiliac
Sacroiliac - Pelvic Pain
 Signs or Symptoms
Signs or Symptoms
Pain or severe ache in the pelvis especially in the back
Description
The pain or ache usually follows a bending type trauma or a fall. The structures that are damaged are the joint, ligaments and muscles.
Causes
Trauma, lifting type injuries, falls
Standard treatment
Rest, ice, anti-inflammatories
AK Approach
The muscles that support the pelvis are evaluated to find the ones that are malfunctioning. These are corrected and then the alignment of the pelvic bones is corrected. The attention is then shifted to the localized structures that are injured and failing to support the pelvic joints properly. These can include specialized treatments for ligaments, muscles, skin and joints. This is followed by an analysis of how the person walks, moves and their occupational positions. Finally, attention is directed to corrective procedures that can help stabilize and strengthen the structures to help prevent future injuries. Nutritional therapies aimed at increasing factors that would speed healing and reduce any inflammation are considered.
Other lifestyle modifications are used to prevent or minimize exacerbating the condition. A specific program for your needs is created.
Sciatica
Sciatica
Signs and Symptoms
Severe pain running from the buttocks down the back of the leg. At times the pain will be less but there will be severe atrophy of some of the leg muscles
Description
There is pressure on one or more of the nerve roots in the lumbar spine. This is usually from a protruding disc.
Causes
This condition usually follows a lifting type of injury where the person is bent over and suddenly feels something go in the back and the pain comes immediately or within hours of the incident. There is usually swelling from the strain of the fibers of the back. These include muscles, ligaments nd the disc structure.
Standard Treatment
RICE - which stands for rest, ice and a support brace. This is accompanied by taking anti-inflammatory medications and at times a muscle relaxant. Failure to respond to this care is followed by physical therapy using ultrasound, muscle stimulation and then at times strengthening exercises if it is chronic. If there is poor response an MRI is performed and surgery may be indicated.
AK Approach
In addition to most of the standard treatment, the structures of the back are tested to find the ones that were weak that allowed the injury to occur. Specific muscle therapies are used to reduce the spasm muscles and you are taught to do some of these at home. Manipulation is performed to align the pelvis and the lumbar spine to equalize the weight on the didsc structures. Dietary recommendations to speed the healing and reduce inflammation are also considered.
Shin Splints
Shin Splints
 Signs or Symptoms
Signs or Symptoms
Severe pain over the front of the tibia, lower leg bone, after running or walking
Description
Inflammation of the attachment of the muscles that attach on the shinbone
Causes
Improper walking or running style
Standard treatment
Anti-inflammatory medications, rest
AK Approach
An evaluation of the gait, style of walking or running is done. First, therapy is aimed at reducing the tightness, trigger points, in the muscles involved. Then the question becomes why or what caused the muscle to become inflamed? Testing of the major muscles used on walking and running are performed to make sure that there is not an imbalance that would lead to faulty foot Ð gait mechanics. These are corrected and therapeutic exercises are given. The foot and ankle are then examined for the need of an orthotic, foot support. Nutritional therapies aimed at increasing factors that would lead to relaxing the muscles and reducing any inflammation is considered.
Other lifestyle modifications are used to prevent or minimize exacerbating the condition. A specific program for your needs is created.
Spondylo
Spondylolithesis
 Signs or Symptoms
Signs or Symptoms
Chronic low back pain
Description
This is a developmental defect where the bone, vertebra, does not fully fuse and join together.
Causes
This is a congenital defect.
Standard treatment
Monitor the problem, exercise, restrict jumping or lifting, surgery if severe
AK Approach
The lumbar spine and pelvis are examined to determine the individual muscle strength of the individual muscles that support the area. The general posture is evaluated to determine if the angle of the pelvis is abnormal contributing to increased forces on the lower lumbar spine. Corrections are aimed at normalizing and reducing these forces. Normal muscle strength and flexibility are the aims of the individualized treatment program that is developed for the patient.
Tarsal
Tarsal Tunnel - Heal or Big Toe Pain
 Signs or Symptoms
Signs or Symptoms
Pain and ache in the foot especially around the great toe
Description
Entrapment, pinching, of a nerve that supplies the big toe area of the foot as it passes around the heel bone. Yhis can cause pain that mimics bunion pain.
Causes
Faulty foot function, dropping of the arches of the foot
Standard treatment
Shoe inserts, injections and in severe cases surgery
AK Approach
The muscles of the foot and ankle are evaluated for proper function. Corrections are aimed at normalizing the muscle functioning of the foot. Therapy is then aimed at strengthening the ligaments and muscles of the foot and the need for orthotic support. Nutritional therapies aimed at increasing factors that would lead to relaxing the muscles and reducing any inflammation is considered.
Other lifestyle modifications are used to prevent or minimize exacerbating the condition. A specific program for your needs is created.
Upper Body
Costochondritis
Costochondritis - Breast Bone Pain
 Signs or Symptoms
Signs or Symptoms
Localized pain or severe ache of the chest where the ribs meet the breastbone.
Description
Inflammation of the cartilage and bones in the chest wall.
Causes
The "official" cause of costochondritis is classified as "idiopathic," or unknown. The most common known cause of costochondritis is a traumatic injury
Standard treatment
Rest, ice and anti-inflammatory medications
AK Approach
Factors that would cause local malfunctioning of the rib attachments are looked for. These are usually imbalances of the muscles that attach to the ribs. The involved muscles are examined and tested for the specific treatment that will reduce the abnormal function of the muscle and normalize the pull of the muscle. Treatment is then aimed at normalizing the function of the ribs and the spine. Factors that will reduce inflammation and speed the recovery are then tested for.
Other lifestyle modifications are used to prevent or minimize exacerbating the condition. A specific program for your needs is created.
Elbow
Impingement Syndrome - Pain on raising the arm
 Signs or Symptoms
Signs or Symptoms
Pain and restriction on raising the arm in front of you.
Description
The arm bone fails to move properly rubbing against the bones at the top of the shoulder slowly shredding the tendon that runs across the top of the shoulder.
Causes
Improper functioning of the muscles of the shoulder, anatomical malformation, arthritic changes in the shoulder joint
Standard treatment
Stretching exercises, anti-inflammatory medications, cortisone and surgery
AK Approach
The muscles that support the arm in its muscular socket are evaluated to find the ones that are malfunctioning. These are corrected and then tested for the need of corrective exercises. The attention is then shifted to the localized structures that are injured and failing to support the shoulder joint properly like the clavicle and the scapula. These can include specialized treatments for ligaments, muscles, skin and joints. Finally, attention is directed to corrective procedures that can help coordinate the muscles to help prevent future injuries. Nutritional therapies aimed at increasing factors that would speed healing and reduce any inflammation are considered.
Other lifestyle modifications are used to prevent or minimize exacerbating the condition. A specific program for your needs is created.
Elbow Problems
Elbow Problems
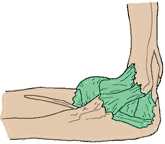 Signs or Symptoms
Signs or Symptoms
Localized soreness and pain around the elbow
Tenderness when doing activities that stress the elbow like golf, tennis, painting
Description
Inflammation of the muscle tendons and ligaments.
Causes
Over use is one of the most common causes. However, many itmes there are weaknesses in the wrist or in the shoulder that cause you to have to overuse the muscles of the forearm. A common problem is improper form in tennis where you do not use your body properly over stressing the elbow.
Standard treatment
Rest, ice, tennis elbow splints and anti-inflammatory medications. If these fail to relieve the symptoms, steroid injections may be used.
AK Approach
The elbow can be injured by either immediate direct trauma or by repeated micro trauma. If the injury occurred from a single trauma, the examination is directed immediately to the severity of the injury. Otherwise, the examination is more general as to the total functioning of the upper extremity. It is rare to find an elbow injury without a preexisting weakness in the legs, torso or shoulder. As the elbow is placed at a disadvantage by a weakness in the legs, torso or shoulder the examination begins by looking for factors in these areas that would adversely affect elbow stability. Locally, the stability of the major ligaments of the elbow is then tested for. The muscles that support the elbow are evaluated to find the ones that are malfunctioning. These are corrected and then tested for the need of corrective exercises.
The attention is then shifted to the localized structures that are injured and failing to support the elbow joint properly. These can include specialized treatments for ligaments, muscles, skin and joints. Finally, attention is directed to corrective procedures that can help coordinate the muscles to help prevent future injuries. Nutritional therapies aimed at increasing factors that would speed healing and reduce any inflammation are considered.
Other lifestyle modifications are used to prevent or minimize exacerbating the condition. A specific program for your needs is created.
Impingement
Impingement Syndrome - Pain on raising the arm
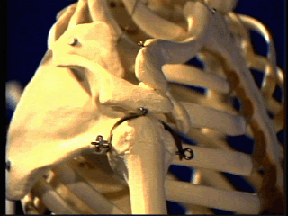 Signs or Symptoms
Signs or Symptoms
Pain and restriction on raising the arm in front of you.
Description
The arm bone fails to move properly rubbing against the bones at the top of the shoulder slowly shredding the tendon that runs across the top of the shoulder.
Causes
Improper functioning of the muscles of the shoulder, anatomical malformation, arthritic changes in the shoulder joint
Standard treatment
Stretching exercises, anti-inflammatory medications, cortisone and surgery
AK Approach
The muscles that support the arm in its muscular socket are evaluated to find the ones that are malfunctioning. These are corrected and then tested for the need of corrective exercises. The attention is then shifted to the localized structures that are injured and failing to support the shoulder joint properly like the clavicle and the scapula. These can include specialized treatments for ligaments, muscles, skin and joints. Finally, attention is directed to corrective procedures that can help coordinate the muscles to help prevent future injuries. Nutritional therapies aimed at increasing factors that would speed healing and reduce any inflammation are considered.
Other lifestyle modifications are used to prevent or minimize exacerbating the condition. A specific program for your needs is created.
Intercostal Neuritis Neuralgia
Intercostal Neuritis Neuralgia
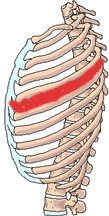 Signs or Symptoms
Signs or Symptoms
Localized pain or severe ache that runs between the ribs.
Description
Entrapment of the nerve that runs between the ribs where the rib meets the spine.
Causes
This is caused by trauma that pinches the nerve causing the inflammation
Standard treatment
Rest, ice and anti-inflammatory medications
AK Approach
Factors that would cause local malfunctioning of the rib attachments are looked for. These are usually imbalances of the muscles that attach to the ribs. The involved muscles are examined and tested for the specific treatment that will reduce the abnormal function of the muscle and normalize the pull of the muscle. Treatment is then aimed at normalizing the function of the ribs and the spine. Factors that will reduce inflammation and speed the recovery are then tested for.
Other lifestyle modifications are used to prevent or minimize exacerbating the condition. A specific program for your needs is created.
Medialepicondylitis
Medial Epicondylitis or golfer
![]() Signs or Symptoms
Signs or Symptoms
Localized pain and ache that is found on the inner side of your elbow
Description
Golfer's elbow is a form of tendonitis or inflammation of the tendons near the elbow joint.
Causes
This is a ligament- muscle condition caused by overuse of the muscles causing the tendon to become inflamed
Standard treatment
Rest, supports, and anti-inflammatories are given.
AK Approach
The elbow can be injured by either immediate direct trauma or by repeated micro trauma. If the injury occurred from a single trauma, the examination is directed immediately to the severity of the injury. Otherwise, the examination is more general as to the total functioning of the upper extremity. It is rare to find an elbow injury without a preexisting weakness in the legs, torso or shoulder. As the elbow is placed at a disadvantage by a weakness in the legs, torso or shoulder the examination begins by looking for factors in these areas that would adversely affect elbow stability. Locally, the stability of the major ligaments of the elbow is then tested for. The muscles that support the elbow are evaluated to find the ones that are malfunctioning. These are corrected and then tested for the need of corrective exercises. The attention is then shifted to the localized structures that are injured and failing to support the elbow joint properly. These can include specialized treatments for ligaments, muscles, skin and joints. Finally, attention is directed to corrective procedures that can help coordinate the muscles to help prevent future injuries. Nutritional therapies aimed at increasing factors that would speed healing and reduce any inflammation are considered. Other lifestyle modifications are used to prevent or minimize exacerbating the condition. A specific program for your needs is created.
Neck Pain
Cervical Radiculitis
Signs and Symptoms
Moderate to severe pain in the neck with radiation down the arm.
Description
The muscles, ligaments and discs of the neck have been injured.
Causes
This condition can occur due to a whiplash type injury or over time from poor posture.
Standard Treatment
RICE - which stands for rest, ice and possibly a support brace. This is accompanied by taking anti-inflammatory medications and at times a muscle relaxant. Failure to respond to this care is followed by physical therapy using ultrasound, muscle stimulation and then at times strengthening exercises if it is chronic.
AK Approach
In addition to most of the standard treatment, the structures of the back are tested to find the ones that were weak that allowed the injury to occur. Specific muscle therapies are used to reduce the spasm muscles and you are taught to do some of these at home. Manipulation is performed to align the spine to equalize the weight on the disc structures. Dietary recommendations to speed the healing and reduce inflammation are also considered. In chronic problems, it is the over all posture that is important. If you have your head forward, the weight of the head will cause arthritic changes and bulging of the disc structures in the neck.
Rotator Cuff
Rotator Cuff
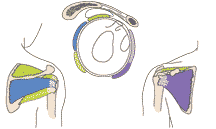 Signs or Symptoms
Signs or Symptoms
Range from an ache to severe pain on moving the arm into a specific position.
Description
The rotator cuff is four muscles that support and move the upper arm bone. Injury to any one of these muscles causes pain, ache, weakness and limited range of motion in the shoulder
Causes
Trauma or repeated abuse.
Standard treatment
Injections, anti-inflammatories, stretching and strengthening exercises. Surgery is done in chronic or severe injuries.
AK Approach
The muscles that support the arm in its muscular socket are evaluated to find the ones that are malfunctioning. These are corrected and then tested for the need of corrective exercises. The attention is then shifted to the localized structures that are injured and failing to support the shoulder joint properly like the clavicle and the scapula. These can include specialized treatments for ligaments, muscles, skin and joints. Finally, attention is directed to corrective procedures that can help coordinate the muscles to help prevent future injuries. Nutritional therapies aimed at increasing factors that would speed healing and reduce any inflammation are considered.
Other lifestyle modifications are used to prevent or minimize exacerbating the condition. A specific program for your needs is created.
Shoulder
Shoulder Problems
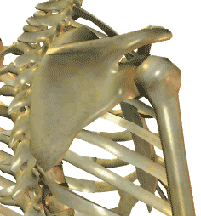 Signs or Symptoms
Signs or Symptoms
Pain, ache or weakness on using your arm
Description
Shoulder injuries run the gamut from ligament injuries, muscle injuries and cartilage damage. The condition can be mild or debilitating as in a frozen shoulder.
Causes
Trauma, whether it is repeated or one severe action is the usual cause
Standard treatment
Physical therapy can run from ultrasound to stretching to exercise to strength the muscles. Cortisone injections, anti-inflammatory medications and if unsuccessful or there is a tear of the cartilage or complete tear of a tendon then surgery
AK Approach
The examination begins with a full investigation of the supporting muscles of the shoulder. As the shoulder is a muscular socket with a bony ball, the muscles are the most integral part. Testing is done to determine that the muscles are functional and can function at any angel the arm is placed at. Treatment is directed to normalize any muscular imbalance, then to ensure proper coordination of function between the muscles. Nutritional therapies aimed at increasing factors that would lead to normalizing the functions of the muscles and reducing any inflammation are considered.
Other lifestyle modifications are used to prevent or minimize exacerbating the condition. A specific program for your needs is created.
Tennis Elbow
Lateral Epicondylitis Tennis Elbow
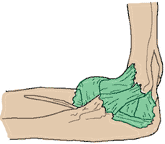 Signs or Symptoms
Signs or Symptoms
Localized pain and ache that is found on the inner side of your elbow
Description
Tennis elbow is a form of tendonitis or inflammation of the tendons near the elbow joint.
Causes
This is a ligament- muscle condition caused by overuse of the muscles causing the tendon to become inflamed.
Standard treatment
Rest, supports, and anti-inflammatories are given.
AK Approach
The elbow can be injured by either immediate direct trauma or by repeated micro trauma. If the injury occurred from a single trauma, the examination is directed immediately to the severity of the injury. Otherwise, the examination is more general as to the total functioning of the upper extremity. It is rare to find an elbow injury without a preexisting weakness in the legs, torso or shoulder. As the elbow is placed at a disadvantage by a weakness in the legs, torso or shoulder the examination begins by looking for factors in these areas that would adversely affect elbow stability. Locally, the stability of the major ligaments of the elbow is then tested for. The muscles that support the elbow are evaluated to find the ones that are malfunctioning. These are corrected and then tested for the need of corrective exercises. The attention is then shifted to the localized structures that are injured and failing to support the elbow joint properly. These can include specialized treatments for ligaments, muscles, skin and joints. Finally, attention is directed to corrective procedures that can help coordinate the muscles to help prevent future injuries. Nutritional therapies aimed at increasing factors that would speed healing and reduce any inflammation are considered. Other lifestyle modifications are used to prevent or minimize exacerbating the condition. A specific program for your needs is created.
Thoracic
Thoracic - Mid Back Pain
Signs and Symptoms
Pain or ache in the middle of the back especially between the shoulder blades
Description
The muscles of the spine have tightened, the ribs are slightly misaligned or possible a disc is bulging.
Causes
This condition usually follows a lifting type of injury where you have been carrying something heavy in your arms, comes from poor posture, or follows a coughing incident.
Standard Treatment
RICE - which stands for rest, ice and possibly a support brace. This is accompanied by taking anti-inflammatory medications and at times a muscle relaxant. Failure to respond to this care is followed by physical therapy using ultrasound, muscle stimulation and then at times strengthening exercises if it is chronic.
AK Approach
In addition to most of the standard treatment, the structures of the back are tested to find the ones that were weak that allowed the injury to occur. Specific muscle therapies are used to reduce the spasm muscles and you are taught to do some of these at home. Manipulation is performed to align the spine and ribs to equalize the weight on the vertebral, bones of the spine, structures. Dietary recommendations to speed the healing and reduce inflammation are also considered. Most important is the strengthening of the muscles that support our posture. Care must be taken to look at the whole posture of the body not just the upper back area.
Thoracicout
Thoracic Outlet Syndrome
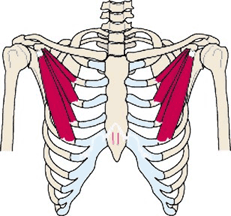 Signs or Symptoms
Signs or Symptoms
Numbness and weakness in the arm - usually worse at night or if carrying objects
Description
The nerves and blood vessels that supply the arm are pinched as they exit the chest cage.
Causes
Weakness of the muscles that support normal posture causes shortening of the muscle that entraps the nerves and blood vessels.
Standard treatment
Stretching of the shortened muscles.
AK Approach
Testing is done to find the weak muscles that are not supporting the posture. These weaknesses are corrected and exercises are givens to strengthen them. Specific muscle therapies are then directed to normalize the length of the pectoralis minor muscle, the muscle that traps the nerves, and to stabilize the normal muscle coordination between the muscles of the front and back of the shoulder. These must be coordinated with an overall approach to normalize the complete posture of the patient. This may involve working on areas from the feet to the jaw muscles.
Other lifestyle modifications, like standing, sitting and sleep postures, are used to prevent or minimize exacerbating the condition. A specific program for your needs is created.
TMJ
TMJ
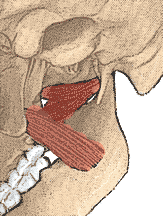 Signs or Symptoms
Signs or Symptoms
Clicking, decreased mouth opening, headaches, tinnitus, ear ringing, dizziness, vertigo
Description
Imbalances in the motion of the jawbone can have far reaching symptomatic effects. These run the gamut from severe headaches to changes in the posture.
Causes
Malocclusion, muscle imbalances, faulty posture
Standard treatment
Muscle relaxants, dental splints, physical therapy to reduce muscle tension
AK Approach
The examination begins with the premise that the head must be level with the ground for the jaw to open properly. Findings that cause head imbalance are found and corrected. The muscles of the jaw are then evaluated for tension and coordinated action. Treatments aimed at equalizing the tension and normalizing the opening and closing of the jaws are then performed. A coordinated treatment program between a qualified chiropractor and dental team may be needed. Other lifestyle modifications are used to prevent or minimize exacerbating the condition. A specific program for your needs is created.
Torticollis
Torticollis - Severe stiff neck
 Signs or Symptoms
Signs or Symptoms
Severe contraction of the neck muscles that prevents turning of the head and neck
Description
The contraction is frequently sudden and severe. It can last for a short time or be permanent.
Causes
The exact cause of this condition is not known. There are many possible causes running from a freak accident, sleeping in an awkward position, to alterations in normal nerve control of the neck muscles.
Standard treatment
Drugs to relax the muscles and reduce inflammation are prescribed. Physical therapy aimed to relax and stretch the muscles is performed.
AK Approach
Tests are performed to isolate muscles that are under functioning. These are then treated to equalize the muscle stress in the neck. This is followed by specific procedures to reestablish the normal muscle function in the neck. These procedures may include spinal manipulation, cranial corrections, specific muscle therapies aimed at normalizing the muscle coordination. Nutritional therapies aimed at increasing factors that would lead to relaxing the muscles and reducing any inflammation is considered. Other lifestyle modifications are used to prevent or minimize exacerbating the condition. A specific program for your needs is created.
Common Conditions
Acne
Acne
Signs or Symptoms
Pimples, Whiteheads, Blackheads, Oily skin, Enlarged pores, Pus filled cyst like pimples.
Description
This condition can range from mild to severe. When severe, it can cause permanent scarring of the skin. It commonly occurs not only on the face but also on the back, neck and buttocks.
This occurs in 3 out of 4 teenagers and is also common in women.
Causes
Acne occurs when the sebaceous glands of the skin produce sebum, a fatty secretion, faster than the pores can excrete it. This along with dead cells creates a plug and blocks the opening of the pore.
The underlying cause of this is an imbalance in hormones. It is during the teenage years that hormone production increases. This condition is also common in women who are supplementing hormones, like taking birth control pills or hormone replacement.
Standard treatment
There are topical and oral treatments for acne. Medications like Retin A and other topically applied agents attempt to dry the pores and kill bacteria on the skin. Oral agents like Accutane and antibiotics maybe used. These have side effects like dry mouth and can cause birth defects if used by pregnant women.
AK Approach Testing is done to determine if there is ways to help balance your hormone system using nutrients to up regulate your ability to detoxify these substances in your liver. Common nutritional deficiencies can make you unable to completely breakdown these hormones. Other lifestyle modifications are used to prevent or minimize exacerbating the acne. A specific program for your needs is created.
Allergies
Allergies
Signs or Symptoms
Itching, hives, watery eyes, swelling around the eyes or lips, runny nose, sneezing, persistent cough withot an elevated temperature, wheezing, chronic breathing problems, nasal congestion, chronic nausea, chronic diarrhea, abdominal cramps
Description
Exposure to an offending substance causes a reaction in the body. This reaction varies from person to person and can affect different systems like the skin, lungs, sinuses, or the digestive tract.
Causes
The most common cause is an over production of histamine.
Standard treatment
Skin patch testing for reactions, medications to block the allergic reaction, desensitization shots
AK Approach
Aside from the histamine response to allergies, there are other organ systems that can play a part in allergies by under functioning. These include your digestive, hormone, and respiratory systems. In addition, the function of you liver, thymus and kidneys can play an important role in controlling symptoms. Testing is done to determine if there are ways to help up regulate the functioning of these systems and organs. . Special tests are done to determine what specific offending agents are upsetting you. Then treatment options ranging from avoidance to desensitization are employed. Other lifestyle modifications are used to prevent or minimize exacerbating the allergic responses. Finally, a specific program for your needs is created.
Asthma
Asthma
Signs or Symptoms
Excessive coughing, wheezing, and difficulty breathing following exposure to an allergen or physical or mental stress.
Description
When people who are sensitive breathe in an allergen, the immune system goes into high gear. The immune system produces a molecule called immunoglobulin E (IgE). The IgE antibody causes mast cells, a type of specialized defensive cell, to release chemical weapons into the airways. The airways then become inflamed and constricted.
Causes
In some people, asthma is an allergic reaction to substances commonly breathed in, such as animal dander, pollen, or dust mite and cockroach waste products. Some people have a genetic predisposition to react to certain allergens. In others, activities like physical exercise can induce the asthma symptoms.
Standard treatment
Corticosteroids can be inhaled to stop an attack. Desensitization may reduce the attacks if the offending agents can be identified.
AK Approach
As with the standard medical treatment, holistic methods to increase your production of specific hormones to increase your breathing capacity are tested for. Other deficiencies that can be easily altered cause the fluid that normally keeps the lung tissues separated to cause sticking of these tissues. Other organ systems can have an adverse effect on your breathing capacity. These include your digestive, immune, cardiac and respiratory systems. Testing is done to determine if there are ways to help up regulate the functioning of these systems and organs. . Special tests are done to determine what specific offending agents are upsetting you. Then treatment options ranging from avoidance to desensitization are employed. Spinal manipulation coupled with breathing exercises can dramatically increase your vital capacity, the amount of air you can breath in. Finally, a specific program for your needs is created.
Bells Palsy
Bell's Palsy - Facial Paralysis
 Signs or Symptoms
Signs or Symptoms
Acute paralysis or weakness on one side of your face Facial droop and difficulty with facial expressions
Facial stiffness
Pain behind or in front of your ear
Headaches
Loss of taste on the front of your tongue
Changes in your production of tears and saliva
Description
Bell's palsy is a weakness, or paralysis, of the muscles that control expression on one side of your face. This results from damage to a facial nerve, one of which runs beneath each ear, near your jaw joint, to the muscles on the same side of your face.
Causes
The cause of Bell's palsy is unknown although many times credited to an infection of the nerve
Standard treatment
The standard treatment is to prescribe a corticosteroid medication and to give time for the nerve to heal.
AK Approach
The nerve that is involved exits the skull near the jaw joint. Imbalances in the bones of the skull or contractions in the muscles of the jaw can cause excessive pressure on this nerve and lead to this condition. Testing is done to determine if there are any imbalances in the motion of the cranial bones or in the functioning of the muscles where the nerve exits. If these are found, very specific corrections are done to remove this stress. Nutritional testing is done to ascertain if there are imbalances that would speed the healing of the nerve.
Cluster Headache
Cluster Headache
 Signs or Symptoms
Signs or Symptoms
Severe migraine type headaches that are localized on one side of the head. They can last from a few hours to days.
Causes
Basically, the cause is unknown
Standard treatment
Medications are given to reduce the intensity of the headache.
AK Approach
The examination begins with local factors in the head. These include testing to determine the normal motion of the bones of the skull, imbalances in the muscles of the jaw, and the tension of the muscles that hold your head on your neck. If there are imbalances that are found, then testing is done to find what is causing the imbalances. Common factors are food sensitivities, environmental factors like perfumes, stress, bite imbalances, hormonal imbalances and spinal, especially neck, problems. The approach is to find the local imbalances that cause the headache and the triggers that cause them to occur. Treatment encompasses both of these aspects by correcting the underlying physical faults and removing or minimizing the triggers. Consequently, cranial corrections, spinal work, balancing of the muscles of the neck, head and especially those of chewing, and nutritional support for aimed at supporting the systems that trigger the headaches are all intertwined into a personalized treatment program.
Fibromyalgia
Fibromyalgia
Signs or Symptoms
Moderate to disabling muscle soreness Ð and fatigue that can occur in an extremity or more commonly over the whole body
Description
Fibromyalgia is a chronic condition where you have widespread muscle and joint pain, fatigue, and multiple tender points in the muscles. Other common symptoms include sleep disturbances, morning stiffness, irritable bowel syndrome and anxiety.
Causes
The cause of fibromyalgia is unknown. The syndrome may be caused by an injury or trauma. Fibromyalgia may be associated with changes in muscle metabolism, such as decreased blood flow, causing fatigue and decreased strength. Some with this syndrome have it triggered by an infectious agent such as a virus.
Standard treatment
Heat and massage give short-term relief. Antidepressant medications may help elevate mood, improve quality of sleep, and relax muscles. Anti-inflammatory medications are also tried.
AK Approach
As this is condition of the whole body, the examination begins with the areas that are most troubling to the patient. The attempt is to reduce musculoskeletal stress so that the local structures do not become inflamed. Different muscle therapies are used to reduce the trigger points. This is followed by a slow progressive exercise routine to increase the ability of the patient to do more without causing inflammation. Nutritional work is done to up-regulate the ability to the body to produce more of its own natural anti-inflammatory compounds. Testing is then done to determine other factors that can lead to an increased inflammation response in the patient. Other lifestyle modifications are used to prevent or minimize exacerbating the condition. A specific program for your needs is created.
Gerd
GERD - Hiatal Hernia - Regurgitation
Signs or Symptoms
Heartburn, pain on swallowing, difficult swallowing, coughing, wheezing, asthma, tooth enamel decay, gingivitis, bad breath, throat soreness, laryngitis, and hoarseness.
Description
Stomach acids come back up into the esophagus and into the mouth irritating these structures.
Causes
Poor functioning of the valve between the stomach and the esophagus, hiatal hernia, slow stomach emptying and decreased salivation are some of the most common causes
Standard treatment
Medications to reduce stomach acidity and in severe cases surgery to reduce the size of the opening between the stomach and the esophagus
AK Approach
The diaphragm is the large muscle that separates the thorax from the abdomen. It wraps around the esophagus and is the major support structure that can be strengthened and used to help prevent the reflux. Testing is done to determine abnormal functioning of the diaphragm. Then treatment is directed at normalizing its function. This is followed by exercises to strengthen any weak structures. Nutritional work to augment the body's own natural anti-inflammatories as well as stimulating healing of the damaged structures is undertaken. Balancing of any imbalances in the normal acid Ð alkaline systems of the body are also tested for and corrective measures undertaken. Other lifestyle modifications are used to prevent or minimize exacerbating the condition. A specific program for your needs is created.
Migraine
Migraine
 Signs or Symptoms
Signs or Symptoms
Severe headache with visual and nauseous symptoms
Description
This is the most severe type of head pain. It is accompanied by visual imbalances and usually with severe gastric upset. It can last for hours or at times days
Causes
As with other common problems, the cause is unknown. It is associated with hormonal imbalances, stress and sensitivities.
Standard treatment
Strong medications to reduce the symptoms are used. These are taken at the first sign that the migraine is starting.
AK Approach
Factors which would cause local malfunctioning of the rib attachments are looked for. These are usually imbalances of the muscles that attach to the ribs. The involved muscles are examined and tested for the specific treatment that will reduce the abnormal function of the muscle and normalize the pull of the muscle. Treatment is then aimed at normalizing the function of the ribs and the spine. Factors that will reduce inflammation and speed the recovery are then tested for. Other lifestyle modifications are used to prevent or minimize exacerbating the condition. A specific program for your needs is created.
Sinus
Sinus
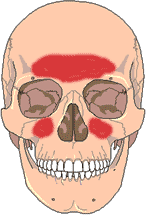 Signs or Symptoms
Signs or Symptoms
Nasal congestion, yellow green discharge, pain in the forehead or behind the eyes or upper cheeks.
Causes
Infection or allergic response in the sinuses
Standard treatment
Antibiotics or antihistamines to reduce fluid production. If severe and chronic - surgery
AK Approach
Local examination is aimed at correcting any imbalance in the cranial bones that would alter the normal drainage from the sinuses. Examination and treatment is then aimed at the underlying cause whether it is an allergic reaction or an infection. Nutritional therapy may by used to augment the immune system. Testing will be done to identify any allergic sensitivity.
Other lifestyle modifications are used to prevent or minimize exacerbating the condition. A specific program for your needs is created.
Tension
Tension Headaches
 Signs and Symptoms
Signs and Symptoms
Pain or ache over the side of the head
Description
This type of headache follows tension situations where the muscles of the neck and side of the head become over contracted.
Causes
This condition usually follows stressful situations, or in persons who clench their teeth.
Standard Treatment
Medications to reduce inflammation, muscle relaxants or mood changing medications like tranquilizers.
AK Approach
In addition to most of the standard treatment, the structures of the neck and skull are tested to find imbalances. Common findings include poor posture, TMJ problems, cranial imbalances and poor response to stress. The treatment program is individualized to address the structural and chemical imbalances in the person. These could run the gamut from environmental sensitivities causing muscle contractions, to strengthening the neck muscles to support the head, to correcting the muscles that hold your jaw, to correcting cranial stress factors, to altering the diet to enable the person to make more stress hormones, to finally teaching the person to do some of the corrections to be better able to handle stress situations.
Tinnitus
Tinnitus - Ringing in the ear
Signs or Symptoms
Continuous or intermittent ringing, buzzing, whistling, roaring, hissing, crackling or other noise in the ear
Description
This is not a condition but a symptom. It is part of almost all ear, TMJ, cardiovascular, thyroid imbalances and head trauma.
Standard treatment
This depends on the underlying cause as outlined above. This care may run the gamut from dental splints to medications to increase blood flow.
AK Approach
The evaluation of the patient includes a full examination of the cranium, skull, the muscles of the jaw, the cervical spine as well as evaluating other visceral problems like lymphatic drainage, blood pressure etc. Treatment is aimed at normalizing the circulation around the ear, reducing muscle spasm in the area, increasing the lymphatic drainage and normalizing other factors like blood pressure. Nutritional therapies aimed at increasing blood flow and decreasing inflammation is considered. Other lifestyle modifications are used to prevent or minimize exacerbating the condition. A specific program for your needs is created.